这构造太抽象了,我做了一天。
解法
观察两个样例发现,所需最小步数是 $n$,考虑如何证明答案下界是 $n$。
这里使用比较经典的容分析,定义每个位置的容为两侧两个相邻和该位置相同的个数,一个状态的容为所有位置的容的和。初始状态的容为 $0$,目标状态的容为 $4 n - 4$,没进行一次操作最多使容增加 $4$,而第一次操作只能将中间的相邻行李移动到两侧的空位上,所以靠外的位置的容没办法增加,而我们期望的本来应该与外侧位置相邻的那个位置的容也没办法增加(就是说只能是内测和与内测相邻的两个位置的容增加),所以第一次移动只能使容增加 $2$,所以答案理论下届为 $n$ 次操作。
考虑如何达到理论下界。
考虑使用暴力搜索找 $n \le 6$ 的规律(因为我这个暴力当 $n=7$ 的时候已经跑不出来了)。
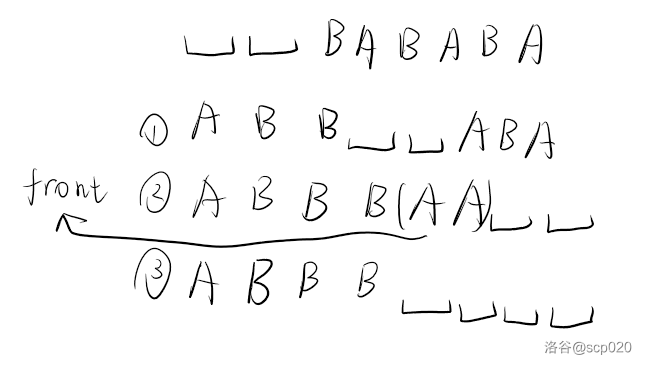
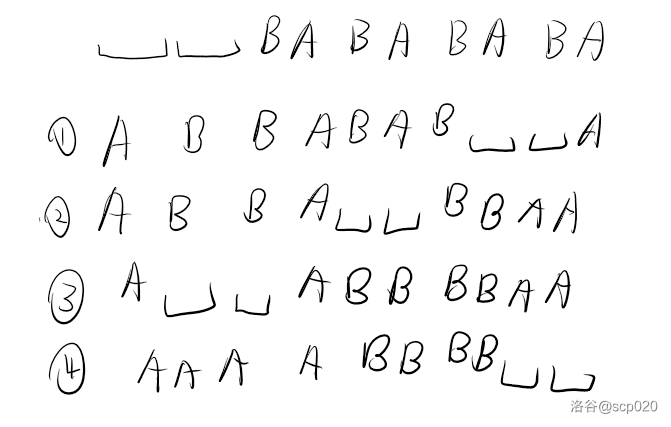


并没有发现什么很直观的规律,故考虑归纳构造。
依次由小到大尝试将 $n$ 仅花费 $x$ 次操作规约为 $n - x$,发现当 $x = 4$ 时可以实现(手玩过程非常漫长),如图。

但是很容易发现 $n = 7$ 的情况不能规约为 $n = 3$ 的情况,否则中间会有两个空位,所以还要手玩一下 $n = 7$ 的情况。

然后就做完了。
代码
暴力核心代码
int n,a[100],ans;
inline bool check2(int l,int r,int val)
{
for(int i=l;i<=r;i++) if(a[i]!=val) return false;
return true;
}
inline bool check()
{
for(int i=0;i<=20;i++) if(a[i]==1) return check2(i,i+n-1,1) && check2(i+n,i+n*2-1,2);
return false;
}
inline void print()
{
for(int i=0;i<=21;i++) out<<a[i]<<' ';
out<<'\n';
}
inline bool dfs(int dep)
{
if(dep==n)
{
if(check())
{
print();
ans++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool flag=false;
for(int i=0,tmp1,tmp2;i<=20;i++)
if(a[i] && a[i+1])
for(int j=0,fl;j<=20;j++)
if(!a[j] && !a[j+1])
{
tmp1=a[i],tmp2=a[i+1],a[j]=a[i],a[j+1]=a[i+1],a[i]=a[i+1]=0,fl=false;
if(dfs(dep+1)) flag=fl=true;
a[j]=a[j+1]=0,a[i]=tmp1,a[i+1]=tmp2;
if(fl) print();
}
return flag;
}
归纳构造代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
namespace fast_IO
{
/**
* useless fastio
*/
};
using namespace fast_IO;
int n;
inline void dfs(int n,int l,int r)
{
if(n==3)
{
out<<l+1<<" to "<<l-2<<'\n';
out<<r-1<<" to "<<l+1<<'\n';
out<<l+2<<" to "<<-3<<'\n';
return;
}
if(n==4)
{
out<<r-2<<" to "<<l-2<<'\n';
out<<l+2<<" to "<<r-2<<'\n';
out<<l-1<<" to "<<l+2<<'\n';
out<<r-1<<" to "<<l-1<<'\n';
return;
}
if(n==5)
{
out<<r-2<<" to "<<l-2<<'\n';
out<<l+2<<" to "<<r-2<<'\n';
out<<r-4<<" to "<<l+2<<'\n';
out<<l-1<<" to "<<r-4<<'\n';
out<<r-1<<" to "<<l-1<<'\n';
return;
}
if(n==6)
{
out<<r-2<<" to "<<l-2<<'\n';
out<<r-5<<" to "<<r-2<<'\n';
out<<l+1<<" to "<<r-5<<'\n';
out<<l+5<<" to "<<l+1<<'\n';
out<<l-1<<" to "<<l+5<<'\n';
out<<r-1<<" to "<<l-1<<'\n';
return;
}
if(n==7)
{
out<<r-6<<" to "<<l-2<<'\n';
out<<l+4<<" to "<<r-6<<'\n';
out<<r-2<<" to "<<l+4<<'\n';
out<<l+2<<" to "<<r-2<<'\n';
out<<r-5<<" to "<<l+2<<'\n';
out<<l-1<<" to "<<r-5<<'\n';
out<<r-1<<" to "<<l-1<<'\n';
return;
}
out<<r-2<<" to "<<l-2<<'\n';
out<<l+2<<" to "<<r-2<<'\n';
dfs(n-4,l+4,r-4);
out<<l-1<<" to "<<r-5<<'\n';
out<<r-1<<" to "<<l-1<<'\n';
}
int main()
{
in>>n;
dfs(n,1,2*n);
fwrite(Ouf,1,p3-Ouf,stdout),fflush(stdout);
return 0;
}